Bortezomib – Multiple Myeloma
Bortezomib
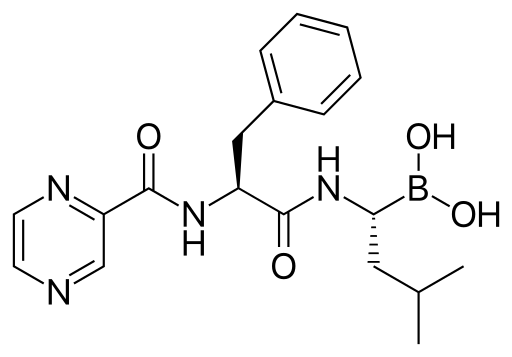
Bortezomib – an innovative antineoplastic agent used for the treatment of multiple myeloma and certain types of lymphoma. Bortezomib belongs to the class of proteasome inhibitors that disrupt the degradation of proteins within cells, leading to the death of rapidly dividing malignant cells such as those found in multiple myeloma. This medication is used as monotherapy or in combination with other anticancer drugs, providing higher treatment response rates. The mechanism of action of Bortezomib involves blocking the activity of the 26S proteasome, which is responsible for degrading ubiquitin-tagged proteins essential for cell division and survival. By inhibiting this process, Bortezomib causes the accumulation of defective proteins, leading to apoptosis (programmed cell death) of cancer cells. It also affects the tumor microenvironment, reducing the growth and survival of malignant plasma cells. Bortezomib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with previously untreated multiple myeloma, as well as for relapsed and refractory cases of the disease. It is also used in the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma in patients who have received prior chemotherapy. The drug is typically administered intravenously or subcutaneously according to a schedule determined by the physician, depending on the stage of the disease, patient condition, and treatment combinations. Potential side effects during therapy may include peripheral neuropathy, nausea, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and fatigue, making regular monitoring and laboratory control essential during treatment. The use of Bortezomib significantly improves survival rates and quality of life for patients with multiple myeloma and other hematologic malignancies, making it a crucial component of modern hematology-oncology treatment regimens.